Tag Archives: cdn for website

Top Reasons To Use CDN For Your Website
-
Danish Ansari
0 Comment
- Digital Updates , WordPress
- benefits of using cdn, cdn around globe, cdn for website, cdn servers, cdn to speed up your website, how cdn works, what is cdn?, why choose cdn for my website
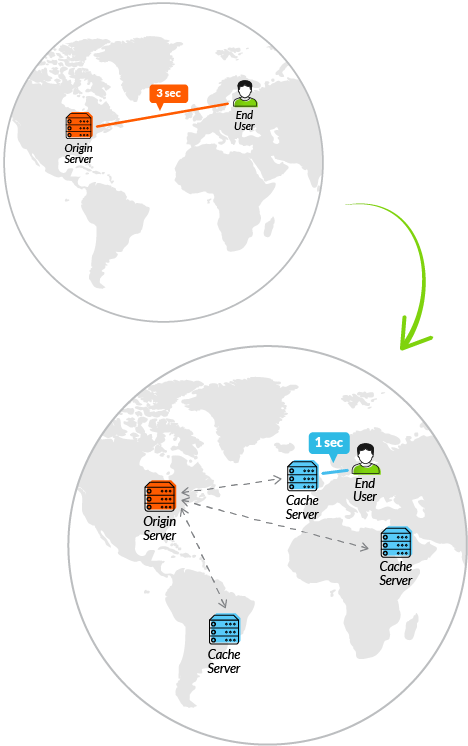
Making your site load faster is one top most important aspect of SEO and internet. According to a study, if your website doesn’t open in 3 seconds, majority of your users leave your website without even taking a look and that’s harsh and tough at the same time for a person who has spent a lot of time and care in building his/her website and than users going away without a glimpse of the website. And to sort this one out, we are going to talk about top reasons to use CDN for your website.
But before proceeding with the reasons, lets know what CDN actually is and how it works?
What is CDN?
Content Delivery Networks (CDN) are the transparent backbone of the Internet in charge of content delivery. Whether we know it or not, every one of us interacts with CDNs on a daily basis; when reading articles on news sites, shopping online, watching YouTube videos or perusing social media feeds.
No matter what you do, or what type of content you consume, chances are that you’ll find CDNs behind every character of text, every image pixel and every movie frame that gets delivered to your PC and mobile browser.
CDN’s are designed to remove Latency, it’s the annoying delay that occurs from the moment you request to load a web page to the moment its content actually appears onscreen.
How CDN works?
To minimize the distance between the visitors and your website’s server, a CDN stores a cached version of its content in multiple geographical locations (a.k.a., points of presence, or PoPs). Each PoP contains a number of caching servers responsible for content delivery to visitors within its proximity.
In essence, CDN puts your content in many places at once, providing superior coverage to your users. For example, when someone in London accesses your US-hosted website, it is done through a local UK PoP. This is much quicker than having the visitor’s requests, and your responses, travel the full width of the Atlantic and back.
This is how a CDN works in a nutshell. Of course, as we thought we needed an entire guide to explain the inner workings of content delivery networks, the rabbit hole goes deeper.
Since, now we have a slightest idea of what CDN is and how it works, lets take a look at,
Top Reasons To Use CDN For Your Website
Performance
What does performance mean? It means connected content delivered at speed. It’s the difference between a click giving you immediate access to new content, and a click then a 7 second wait while a page loads or a video buffers.
How does it work? When requested content is cached (pre-saved) by a CDN’s servers, end users will get that content by connecting to the nearest CDN server rather than waiting for their request to go directly to the origin. This results in a significant performance improvement for the end user. For example, let’s say that Fashion House X (FHX) from Milan, Italy, releases its new line-up for online orders. Fashion lovers in New York, Paris, Rio De Janeiro, and Tokyo all go online to make their orders. If FHX isn’t using a cloud content management system, the request from each end user must go all the way to Milan and back. However, if FHX uses a CDN and has pre-warmed its content across the CDN, each user can access the new content from servers directly in their city, saving their data hundreds or thousands of miles in round-trip time.
What if the content isn’t already in cache? When a CDN server does not have the content in its cache, it is able to traverse the length and breadth of the Internet using its programmed knowledge of the inter-connections between itself and its companion CDN servers. This helps it overcome the challenges of peering between multiple ISPs, lost packets due to network outages, and the time lost in DNS resolution. Advanced CDNs also have other specific technologies to deal with dynamic, or uncacheable, content.
All of this means that via a CDN, content providers can deliver fast, quality web experiences to all their end users; no matter what location, browser, device, or network they’re connecting from. Webpages render faster, video buffering time is reduced, users stay more engaged, and content providers get more business!
Availability
Availability means that content remains accessible to end users under high-stress situations such as excessive user traffic, intermittent spikes, and potential server outages.
When traffic loads peak at millions of requests per second, even the most powerful origin servers would be put to the test. Without a CDN, all this traffic has to be absorbed by a content provider’s origin infrastructure. This can cause the origin to fail, resulting in a terrible end user experience and lost business. That’s when CDNs, with their massively distributed server infrastructure, are of immense value. Advanced CDNs, with their highly distributed architecture and massive server platforms can absorb tens of TBps of traffic and make it possible for content providers to stay available to larger user bases than otherwise possible.
As an example, let’s return to Fashion House X (FHX) in Milan. FHX’s brand is beloved by millions of fashion lovers, and their new line-up generates a lot of excitement. At the moment of launch, fashion lovers from all over the world go online to FHX’s website at the same moment. If FHX is not using a CDN, all of those users would hit their origin server at the same time, causing it to fail. However, if FHX is using a CDN, all of that traffic will be served across the CDN’s hundreds of thousands of servers, keeping FHX’s origin from failing and delivering a quality experience to fashion lovers across the globe.
Security
As the volume of high-value data and transactions on the Internet continues to grow, so do the forces of attackers looking to exploit it – and these forces are costing organizations big money. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute of Cyber Crime, in 2015 businesses around the world suffered average losses of $7.7 million due to cybercrime. Along with crimes committed by malicious insiders, DDoS and web-based attacks were found to be the costliest.
According to a Report, the number of both DDoS attacks and web-based exploits (SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and local or remote file-inclusion attacks) are becoming more common as well. These attacks are also increasingly launched in conjunction using a DDoS to divert attention while causing more serious damage with other exploits. In both types of attacks, it is often difficult to distinguish bad traffic from legitimate traffic, and strategies continue to evolve rapidly over time, requiring significant dedicated security resources in order to stay up to date on mitigation strategies.
Given the increasing volatility of the Internet threat landscape, helping to secure websites is a critical CDN requirement. Today’s most advanced CDNs have made information security a core competency, providing unique cloud-based solutions. CDNs should protect content providers and users by mitigating against a wide array of attacks without malicious entities ever compromising delivery and availability.
Intelligence
As carriers of nearly half of the world’s Internet traffic, CDN providers generate vast amounts of data about end user connectivity, device types, and browsing experiences across the globe. They can expose this data to their customers, thus giving them critical, actionable insights, and intelligence into their user base.Tthis includes Real-User Monitoring and Media Analytics to measure end-user engagement with web content, and Cloud Security Intelligence to keep track of online threats.
Wrapping Up
CDN’s certainly is the solution to high pings and latency’s people are facing while accessing the web and putting CDN in use will make your site load faster and give your user a mesmerizing web experience.Now, choosing a better CDN system is the real challenge because there are a lot of companies out in the market promising something else and reality is quite different. So, we’ll recommend you to choose wisely out of all the available options.
Here’s a list of all free CDN’s which promises up to the mark service quality.
Hope you have enjoyed this blog post and our other blogs as well.
In case if you have missed reading, go through Top 10 Most Illustrated Web Designs or Top 10 Ways To Get More Views On YouTube Videos.
Most Common Web Design Mistakes – Coffin For A Website is a monstrous dream for any web designer.